

However, the performance of existing CAD for identifying COVID-19 and associated pneumonia on CXRs has been scarcely investigated. The term pneumatocele is used to describe a lungcyst, which is most frequently caused by acute pneumonia, trauma, or aspiration of hydrocarbon fluid and is usually transient.Chest X-rays (CXRs) can help triage for Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) patients in resource-constrained environments, and a computer-aided detection system (CAD) that can identify pneumonia on CXR may help the triage of patients in those environment where expert radiologists are not available. In consolidation there should be no or only minimal volume loss, which differentiates consolidation from atelectasis.Įxpansion of a consolidated lobe is not so common and is seen in Klebsiella pneumoniae and sometimes in Streptococcus pneumoniae, TB and lung cancer with obstructive pneumonia. Lobar consolidation is the result of disease that starts in the periphery and spreads from one alveolus to another through the pores of Kohn.Īt the borders of the disease some alveoli will be involved, while others are not, thus creating ill-defined borders.Īs the disease reaches a fissure, this will result in a sharp delineation, since consolidation will not cross a fissure.Īs the alveoli that surround the bronchi become more dense, the bronchi will become more visible, resulting in an air-bronchogram (arrow).
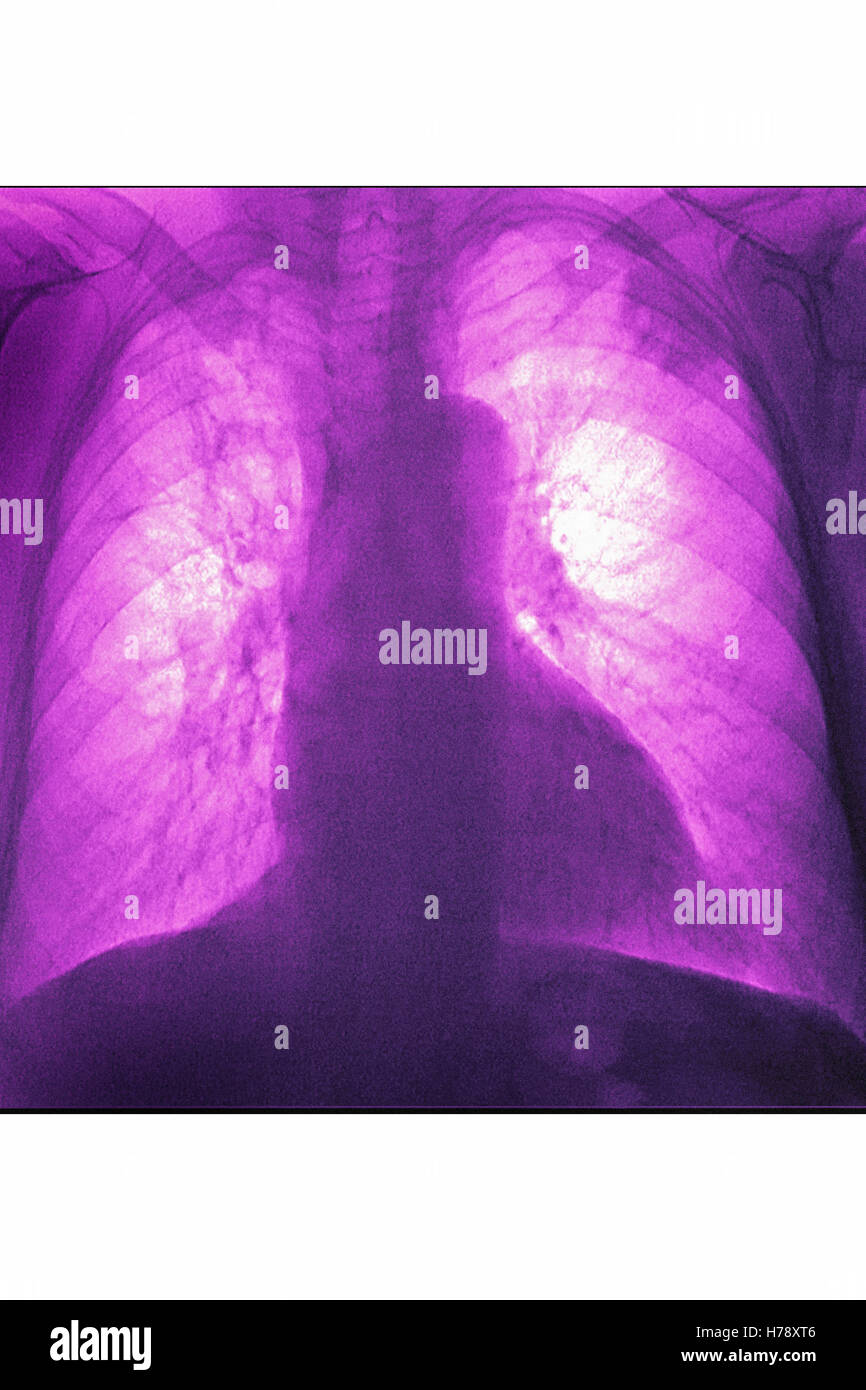
Now it is obvious that some diseases can have more than one pattern.įor instance a lobar pneumonia caused by streptococcus pneumoniae may become diffuse if the patient does not respond to the treatment. Multiple - usually multiple ill-defined densities.Diffuse - perihilar (batwing) or peripheral (reversed batwing).The table summarizes the most common diseases, that present with consolidation.Ī way to think of the differential diagnosis is to think of the possible content of the alveoli:Īnother way to think of consolidation, is to look at the pattern of distribution: Fleischner Society recommendations for follow-up of nodules.In this article we will focus on this four-pattern approach.Īt the end we will also discuss diseases that present as areas of decreased density. Lung abnormalities with an increased density - also called opacities - are the most common.Ī practical approach is to divide these into four patterns: On a chest x-ray lung abnormalities will either present as areas of increased density or as areas of decreased density. White Matter Lesions - Differential diagnosis.

Xray pneumonia how to#
How to Differentiate Carotid Obstructions.TI-RADS - Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System.Esophagus II: Strictures, Acute syndromes, Neoplasms and Vascular impressions.Esophagus I: anatomy, rings, inflammation.Vascular Anomalies of Aorta, Pulmonary and Systemic vessels.Contrast-enhanced MRA of peripheral vessels.Ischemic and non-ischemic cardiomyopathy.Coronary Artery Disease-Reporting and Data System 2.0.Bi-RADS for Mammography and Ultrasound 2013.Transvaginal Ultrasound for Non-Gynaecological Conditions.Acute Abdomen in Gynaecology - Ultrasound.Appendicitis - Pitfalls in US and CT diagnosis.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
